Product Description:
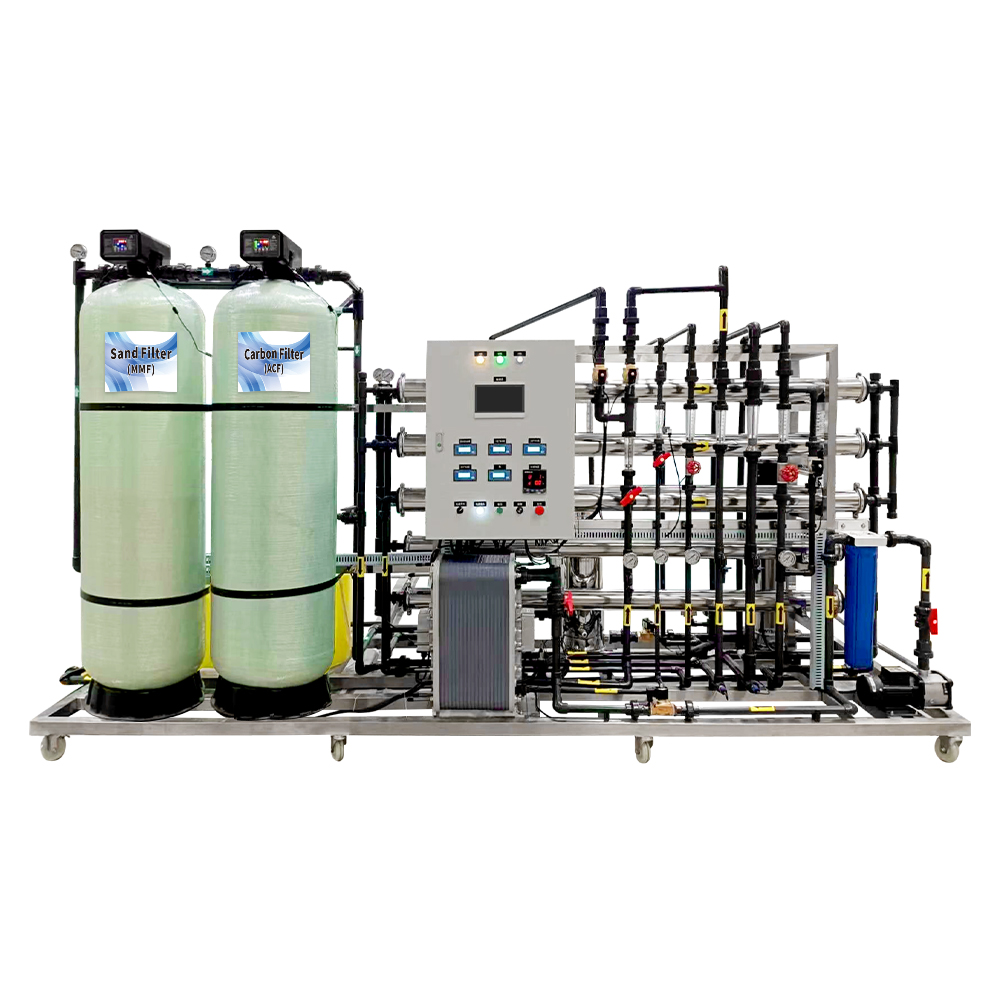
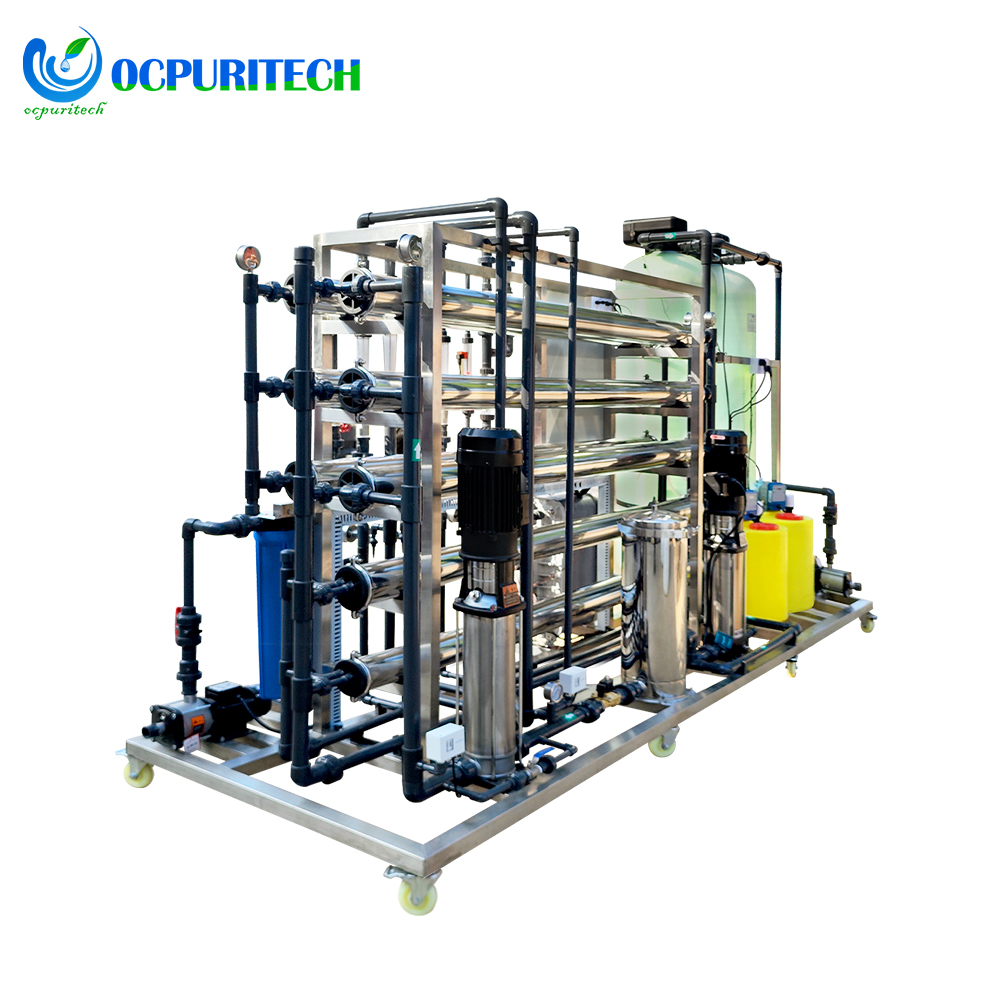
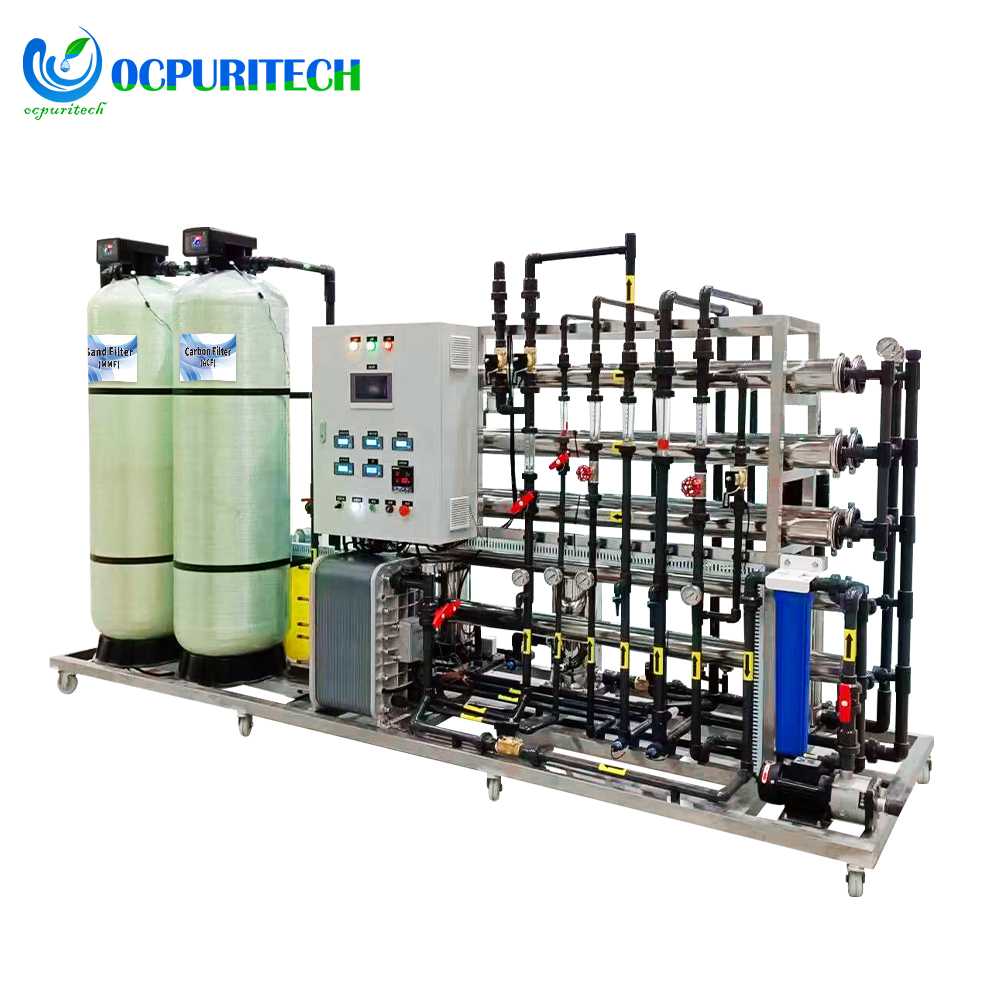
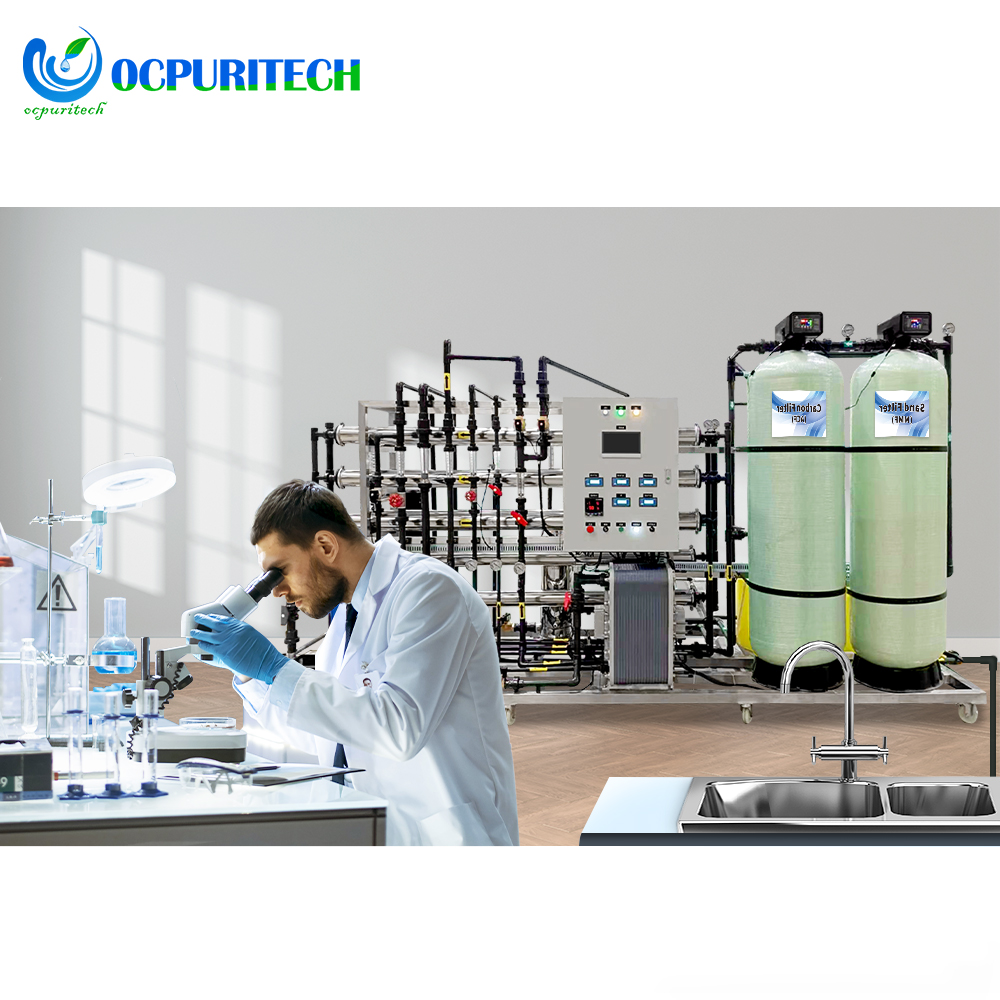
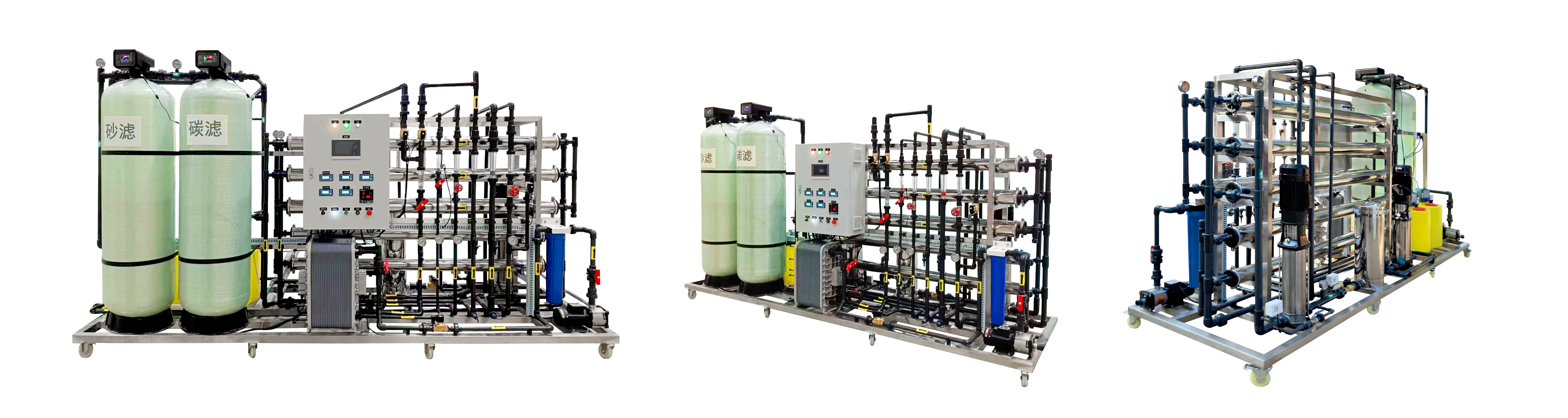
This RO water treatment system features a robust stainless steel frame for durability and stability. The pressure gauge accurately reads 1.0MPa, ensuring reliable operating pressure. A 7-inch touchscreen simplifies operation and provides an intuitive monitoring interface. With 25kg of anti-scaling agent, it effectively prevents scale formation, extending the system’s lifespan. Additionally, the 40L measurement box facilitates convenient and quick addition of the anti-scaling agent, ensuring efficient system operation.
Key Features:
- Robust stainless steel frame for durability and stability
- Accurate pressure gauge reading of 1.0MPa for reliable operation
- 7-inch touchscreen for simplified operation and intuitive monitoring
- 25kg of anti-scaling agent effectively prevents scale formation, extending system lifespan
- 40L measurement box facilitates convenient addition of anti-scaling agent for efficient operation
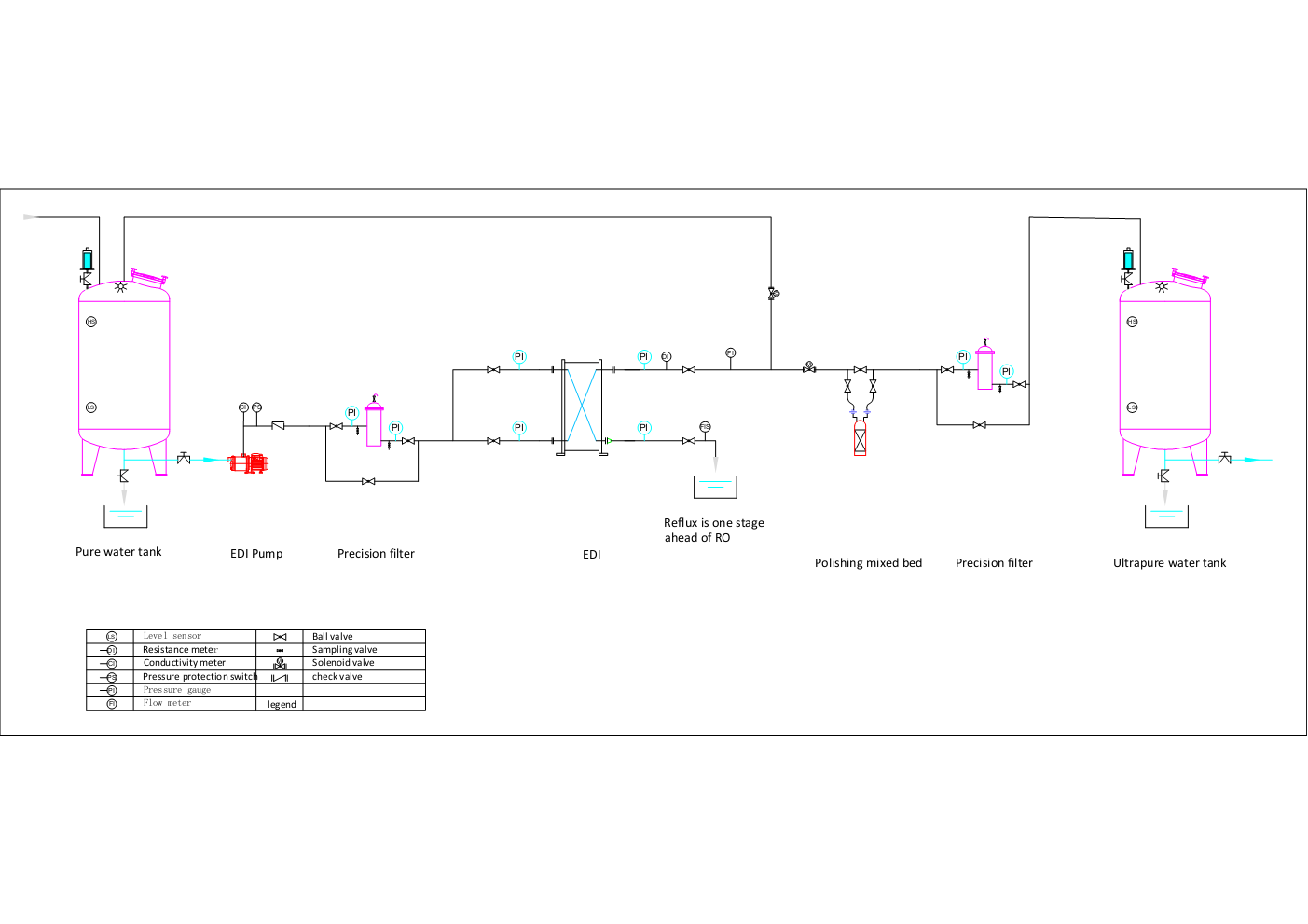
The EDI (Electrodeionization) process is a water treatment technology that removes ions from water using electricity. Here’s a simplified explanation of the EDI process:
- Feed Water Intake: Water enters the EDI system from a water source such as a municipal supply or a pretreatment system.
- Pre-treatment: Before entering the EDI module, the feed water undergoes pre-treatment to remove particulates, organic matter, and other impurities. This step typically involves filtration and chemical treatment to optimize water quality for the EDI process.
- Electrodeionization Module: The pre-treated water flows into the EDI module, which consists of alternating ion exchange resin beds and electrode chambers. When an electric current is applied, ions in the water are attracted to oppositely charged electrodes, effectively removing them from the water stream.
- Ion Exchange: Within the module, ions are exchanged between the ion exchange resin and the water. Cations (positively charged ions) migrate towards the negatively charged electrode (cathode), while anions (negatively charged ions) migrate towards the positively charged electrode (anode). This continuous ion exchange process results in the removal of dissolved ions from the water.
- Product Water Collection: The purified water, now depleted of ions, exits the EDI module as product water. This water is typically of high purity and suitable for various industrial and commercial applications, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, power generation, and semiconductor fabrication.
- Concentrate Discharge: The concentrated stream containing ions removed from the feed water, known as the concentrate or reject stream, exits the EDI module separately. This concentrate may undergo further treatment or be discharged in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Overall, the EDI process offers a continuous and chemical-free method for producing high-purity water by leveraging the principles of ion exchange and electrochemical reactions.